1 how do things move without contact?
1.0.1 inverse square law
inverse square law states that if the distance is increased by a factor of \(a\), then the force is decreased by a factor of \(a^2\).
\[F\propto{\frac{1}{r^2}}\]
1.1 gravitational
| name | symbol | units |
|---|---|---|
| mass | \(M,m\) | \((kg)\) |
| gravitational field strength | \(g\) | \((Nkg^{-1})(ms^{-2})\) |
| gravitational constant | \(G\) | \((m^3kg^{-1}s^{-2})\) |
| gravitational force | \(F_g\) | \((N)\) |
| gravitational potential energy | \(E_g\) | \((J)\) |
\[G=6.67\times{}10^{-11}\]
\[g=\frac{GM}{r^2}\]
\[F_g=mg=\frac{GMm}{r^2}\]
\[E_g=mg\Delta{h}\]
1.1.1 kepler’s law
kepler’s law states that the period of orbit square divided by the radius of orbit cubed is a constant.
\[\frac{T^2}{r^3}=\frac{4\pi^2}{GM}\]
1.2 electrical
| name | symbol | units |
|---|---|---|
| charge | \(Q,q\) | \((C)\) |
| electrical field strength | \(E\) | \((NC^{-1})(Vm^{-1})\) |
| coulomb’s constant | \(k\) | \((Nm^2C^{-2})\) |
| electric force | \(F_e\) | \((N)\) |
| voltage | \(V\) | \((V)\) |
| distance | \(d\) | \((m)\) |
| work done | \(W\) | \((J)\) |
\[Q_{proton}=1.6\times{}10^{-19}\]
\[m_{electron}=9.1\times{}10^{-31}\]
\[k=\frac{1}{4\pi{}\varepsilon_0}=8.987\times{}10^9\]
\[E=\frac{kQ}{r^2}\]
\[F_e=qE=\frac{kQq}{r^2}\]
\[W=fd=qV\]
1.3 magnetic
| name | symbol | units |
|---|---|---|
| charge | \(q\) | \((C)\) |
| velocity | \(v\) | \((ms^{-1})\) |
| magnetic field strength | \(B\) | \((T)\) |
| number of loops | \(n\) | |
| current | \(I\) | \((A)\) |
| length | \(l\) | \((m)\) |
1.3.1 lorentz force \((N)\)
\[F_m=qvB\]
\[F_m=nilB\]
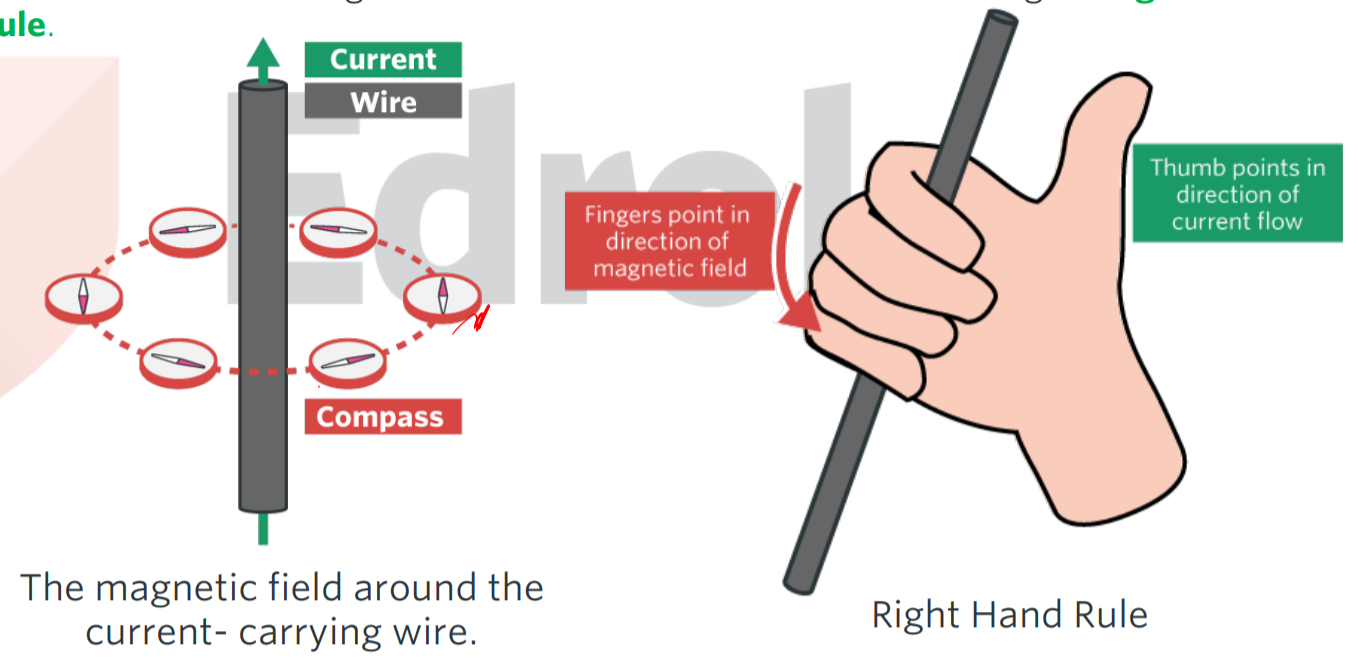
right hand grip rule
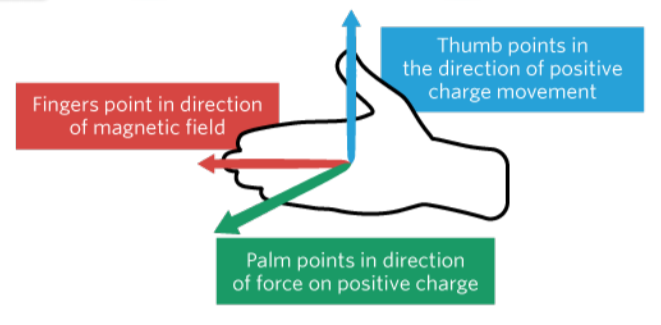
right hand lorentz rule
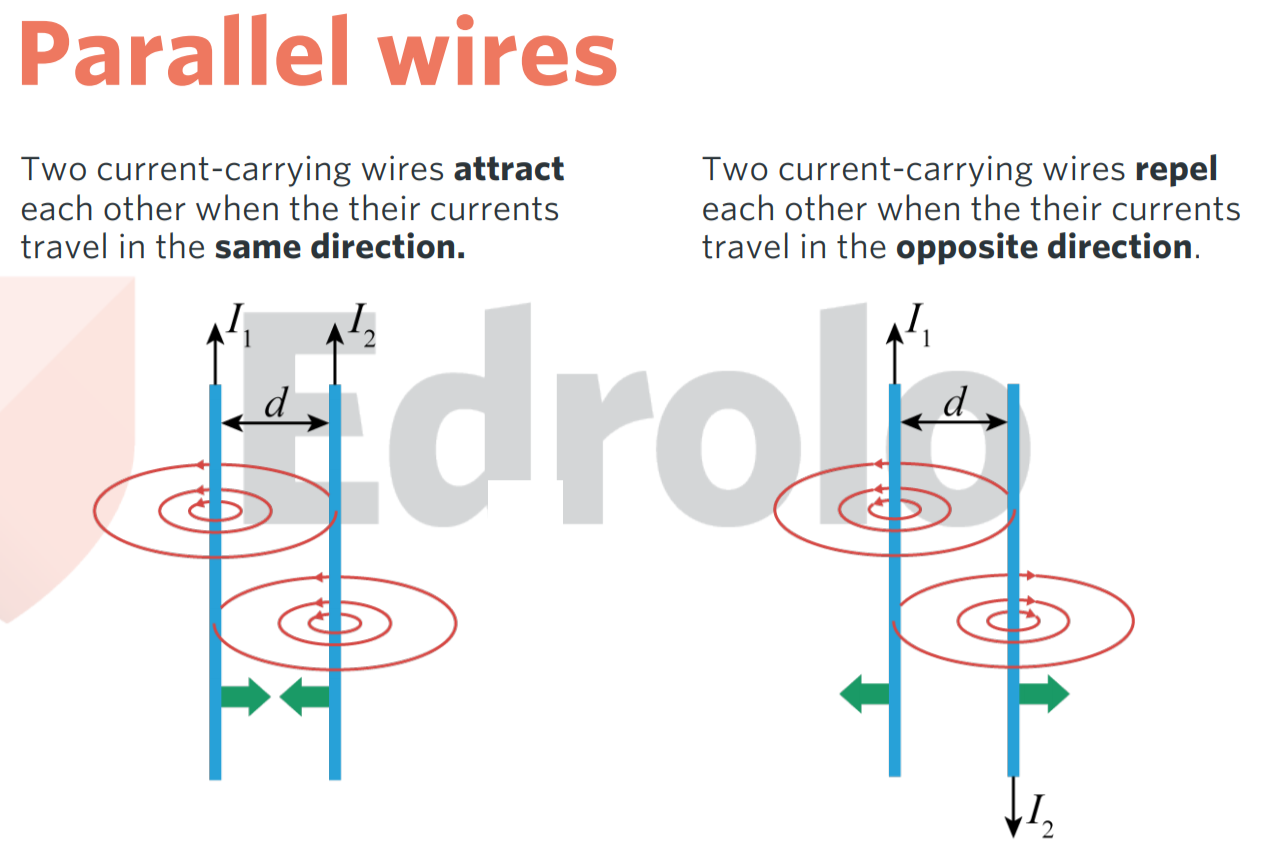
parallel current carrying wires